Canon’s L-Series lenses have long been revered by professional photographers and enthusiasts alike for their exceptional quality and performance. In this comprehensive guide, we will delve into the world of Canon’s L-Series lenses, exploring what makes them stand out from the crowd. From superior optics to robust build quality, these lenses are a testament to Canon’s commitment to excellence. So, let’s embark on this journey to uncover the secrets of Canon’s L-Series lenses.
Introduction to Canon’s L-Series Lenses
Canon’s L series lenses are the company’s top-tier lineup, known for their exceptional build quality, optical performance, and professional features. They stand out significantly from Canon’s standard range of lenses due to several advanced technologies and manufacturing processes that enhance image quality, durability, and usability.

Here’s a detailed breakdown of what makes Canon L series lenses different:
1. Optical Glass Elements
- Ultra-low Dispersion (UD) and Super UD Elements: L series lenses frequently use UD and Super UD glass elements to minimize chromatic aberration, ensuring sharper images with better color fidelity. These elements help to correct color fringing and distortion, particularly at longer focal lengths and wider apertures.
- Fluorite Elements: Some L lenses, especially telephoto models, incorporate fluorite glass elements. Fluorite has lower dispersion characteristics than standard optical glass, which significantly reduces chromatic aberration and improves contrast and resolution.
- Aspherical Elements: Many L series lenses feature aspherical elements, which correct spherical aberrations and reduce distortion. These elements are particularly important in wide-angle and zoom lenses to maintain sharpness across the entire image frame.
This is how the DO part of Canon lenses works, making sure that light at different wavelengths converges on a single point.
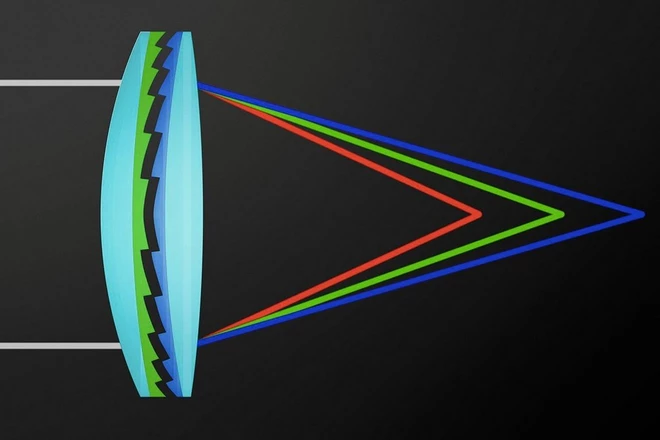
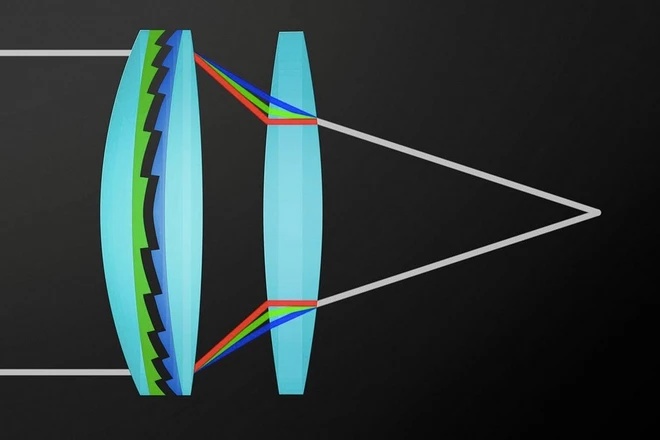
2. Advanced Lens Coatings
- Super Spectra Coating: This is a standard coating applied to all Canon lenses, but L series lenses receive advanced versions that are more effective at reducing reflections, flare, and ghosting. The coating enhances color balance and increases contrast by minimizing internal reflections.
- Subwavelength Structure Coating (SWC): Introduced in some L series lenses, SWC uses microscopic cone-shaped structures to reduce reflections more effectively than traditional coatings. It is particularly useful in wide-angle lenses where internal reflections can cause significant image degradation.
- Air Sphere Coating (ASC): Another advanced coating used in select L series lenses, ASC combines a traditional multi-layer coating with an ultra-low refractive index layer. This further reduces ghosting and flare, especially in backlit conditions, resulting in clearer, more contrast-rich images.
- Fluorine Coating: L series lenses often feature fluorine coatings on the front and rear elements. This coating repels water, oil, and dust, making it easier to clean the lens and maintain image quality over time.
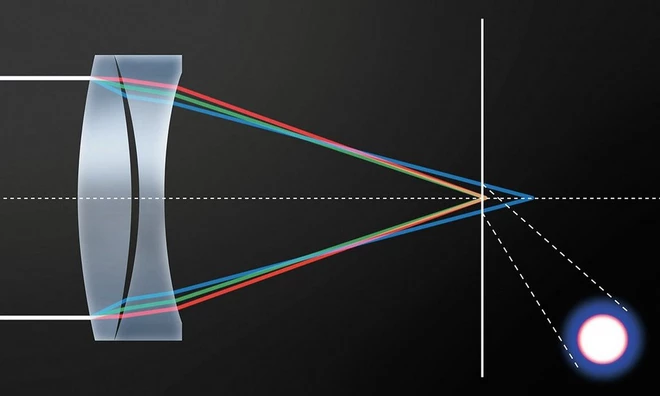
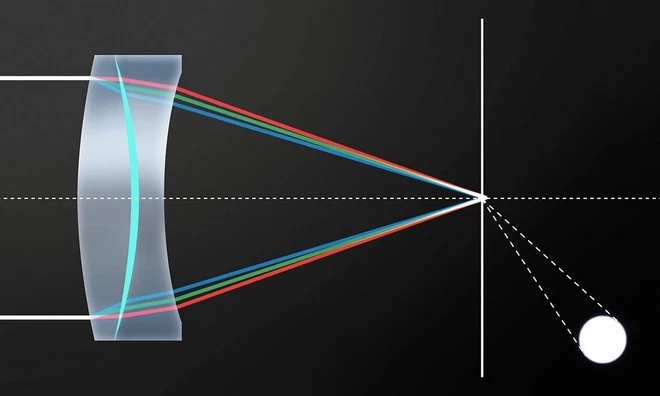
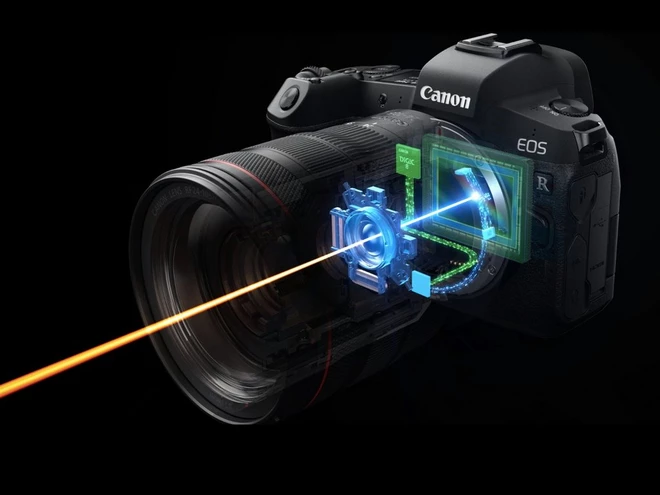
3. Manufacturing Precision and Quality Control
- Hand Assembly and Testing: L series lenses undergo more rigorous quality control and are often hand-assembled. Each lens is tested for optical performance, including sharpness, chromatic aberration, and focus accuracy. This level of scrutiny ensures that each lens meets Canon’s high standards.
- Tighter Tolerances: During the manufacturing process, L series lenses are built to much tighter tolerances than standard lenses. This ensures that all elements are precisely aligned, which is critical for maintaining optical performance, particularly in high-resolution applications.
- Advanced Materials: L series lenses often use more robust materials such as magnesium alloy for the lens body and mounts, providing greater durability and a premium feel. This construction helps to withstand professional use and adverse environmental conditions.
4. Weather-Sealing and Durability
- Weather-Resistant Design: Most L series lenses feature extensive weather-sealing to protect against dust, moisture, and temperature changes. Rubber gaskets are used at critical points, such as the lens mount, focus ring, and zoom ring, making them suitable for use in challenging environments.
- Enhanced Durability: The use of high-grade materials like magnesium alloy and the reinforced lens barrels ensure that L series lenses can withstand rough handling and heavy use without compromising performance.
5. Aperture and Autofocus Technologies
- Circular Aperture Blades: L series lenses often have more rounded aperture blades, typically 8 to 9, which create a more pleasing bokeh (background blur) compared to standard lenses that may use fewer or less rounded blades. This is particularly beneficial for portraiture and selective focus techniques.
- Ultrasonic Motor (USM): Many L series lenses use advanced ring-type USM motors for fast, silent, and accurate autofocus. This is superior to the micro USM or stepping motors found in many standard lenses, providing better performance for both stills and video.
- Nano USM and Dual Nano USM: Some newer L series lenses incorporate Nano USM or Dual Nano USM motors, which offer even smoother and more precise focusing. These are particularly beneficial for video applications, providing silent operation and seamless focus transitions.
- Focus Limiter Switches and Full-Time Manual Focus (FTM): L series lenses often include focus limiter switches that allow photographers to restrict the focusing range, speeding up autofocus in certain situations. They also feature full-time manual focus, enabling manual adjustments without switching from AF to MF mode.
6. Specialized Features in Certain L Series Lenses
- Image Stabilization (IS): L series lenses feature advanced IS systems with multiple modes, including normal, panning, and tripod modes. Some lenses have 4- or 5-stop IS systems, providing excellent stabilization for low-light and handheld shooting.
- Hybrid IS: In macro L lenses, such as the EF 100mm f/2.8L Macro IS USM, hybrid IS compensates for both angular and shift camera movements, which are particularly pronounced at close distances.
- Internal Focusing and Zoom Mechanisms: Many L lenses use internal focusing and zooming, meaning the lens length doesn’t change when focusing or zooming. This design helps maintain balance and makes it easier to use with filters and accessories.

7. Design and Aesthetics
- Iconic Red Ring: The red ring on L series lenses is a visual indicator of their professional status and quality. It has become a symbol of excellence and high performance among photographers.
- Professional Aesthetic: L series lenses are designed to look and feel professional, with a focus on functionality, ergonomics, and durability. The matte finish, robust build, and smooth operation of focus and zoom rings contribute to their professional appeal.
Canon L Series vs Competitors
Comparing Canon’s L series lenses to professional lens offerings from Nikon, Sony, and Fujifilm involves a detailed examination of various aspects such as optical design, build quality, autofocus technology, lens coatings, and overall performance. Each brand has its strengths, and the “superiority” can depend on specific use cases and preferences. Below is a granular comparison of Canon L series lenses against Nikon’s NIKKOR, Sony’s G Master, and Fujifilm’s XF lenses.
1. Optical Design and Glass Elements
Canon L Series
- Elements and Construction: Canon L lenses often use multiple aspherical elements, Ultra-low Dispersion (UD), and Super UD glass elements. Some telephoto models incorporate fluorite elements, which are superior in reducing chromatic aberration compared to standard optical glass.
- Signature Features: Many L series lenses are known for their “Zero-D” (near-zero distortion) performance, particularly in wide-angle lenses, which is a significant advantage in architectural and landscape photography.
Nikon NIKKOR (S-Line for Mirrorless)
- Elements and Construction: Nikon employs ED (Extra-low Dispersion), Super ED, and aspherical elements. In some high-end lenses, they use fluorite and SR (Short-wavelength Refractive) elements, designed to correct chromatic aberrations more effectively.
- Signature Features: Nikon’s PF (Phase Fresnel) technology is used in select lenses, like the AF-S NIKKOR 300mm f/4E PF ED VR, to reduce the size and weight of telephoto lenses without sacrificing optical quality.
Sony G Master (GM)
- Elements and Construction: G Master lenses use XA (extreme aspherical) elements, Super ED, and ED elements. The use of XA elements helps achieve extremely smooth bokeh and high resolution across the frame.
- Signature Features: Sony’s GM lenses are known for their exceptional resolution and smooth bokeh, thanks to their advanced optical design, which includes tighter manufacturing tolerances for aspherical elements than typically seen in the industry.
Fujifilm XF and GF (for Medium Format)
- Elements and Construction: XF lenses for APS-C and GF lenses for medium format often use ED and aspherical elements. Their medium format lenses incorporate Super ED glass to minimize aberrations at a larger scale.
- Signature Features: Fujifilm emphasizes edge-to-edge sharpness and minimal distortion, leveraging their film simulation modes and color science, which can be especially impactful in combination with their lenses.
2. Lens Coatings
Canon L Series
- Coating Technologies: Canon uses advanced coatings like Super Spectra Coating, Subwavelength Structure Coating (SWC), and Air Sphere Coating (ASC). These coatings reduce flare and ghosting significantly and are especially effective in countering reflections and enhancing contrast in backlit conditions.
- Fluorine Coating: Applied to front and rear elements for easy cleaning and protection against oil and water.
Nikon NIKKOR
- Coating Technologies: Nikon’s Nano Crystal Coat and ARNEO Coat are used to combat flare and ghosting. The ARNEO coat is particularly effective against light entering the lens at an angle, while Nano Crystal Coat handles perpendicular light.
- Fluorine Coating: Nikon also applies fluorine coatings for easier maintenance, similar to Canon.
Sony G Master
- Coating Technologies: Sony uses Nano AR Coating to minimize reflections, flare, and ghosting. Their coating technology is effective, but some users have reported more susceptibility to flare compared to Canon and Nikon lenses in extreme conditions.
- Fluorine Coating: Sony applies fluorine coatings on their more expensive lenses to ensure durability and easy maintenance.
Fujifilm XF and GF
- Coating Technologies: Fujifilm uses HT-EBC (High Transmittance Electron Beam Coating) to reduce flare and ghosting. The coatings are generally effective, but Fujifilm lenses may have slightly less resistance to flare compared to Canon’s SWC or Nikon’s ARNEO Coating in extreme backlit conditions.
- Fluorine Coating: Available on select XF and GF lenses, providing similar benefits to those found in Canon and Nikon lenses.
3. Autofocus Systems
Canon L Series
- Technology: Canon uses various AF motors, including Ring-type Ultrasonic Motors (USM), Nano USM, and Stepping Motors (STM). The latest RF L lenses for mirrorless systems incorporate Dual Nano USM for even smoother and quieter autofocus.
- Performance: L series lenses are known for fast, accurate, and quiet focusing. The Dual Nano USM is particularly effective in combining fast speed with smooth operation, making it suitable for both stills and video.
Nikon NIKKOR
- Technology: Nikon employs Silent Wave Motor (SWM) in F-mount lenses and Stepping Motor (STM) or Voice Coil Motors (VCM) in Z-mount lenses for mirrorless systems.
- Performance: Nikon’s newer Z-mount lenses, particularly S-Line, offer fast and silent autofocus, comparable to Canon’s L series in terms of speed and accuracy. Nikon’s AF performance is often praised for its reliability in low light.
Sony G Master
- Technology: G Master lenses use Direct Drive Super Sonic wave Motors (DDSSM) and Linear Motors for fast and precise focusing. Some lenses also use XD Linear Motors, which are even faster and more accurate.
- Performance: Sony’s autofocus system is renowned for its speed, precision, and silence, especially when paired with their advanced AF systems in mirrorless cameras. Sony GM lenses often have the edge in tracking moving subjects.
Fujifilm XF and GF
- Technology: Fujifilm uses a mix of linear motors and stepping motors in their lenses. In recent lenses, they’ve introduced LM (Linear Motor) for faster focusing.
- Performance: While Fujifilm’s AF systems have improved significantly, they still lag behind Canon, Nikon, and Sony in terms of autofocus speed and reliability, especially in low-light conditions or with fast-moving subjects.
4. Build Quality and Weather-Sealing
Canon L Series
- Build Quality: L series lenses are known for their robust construction, typically using high-quality metal bodies, and often incorporating magnesium alloy for lightweight durability.
- Weather-Sealing: Most L series lenses are extensively weather-sealed, including gaskets around the lens mount and additional sealing around buttons and rings. This makes them highly reliable in challenging weather conditions.
Nikon NIKKOR
- Build Quality: High-end NIKKOR lenses, especially those in the S-Line and professional F-mount lenses, use durable metal and composite materials. They are built to withstand professional use and abuse.
- Weather-Sealing: Professional NIKKOR lenses feature comprehensive weather-sealing, comparable to Canon’s L series. This includes sealing against dust and moisture, ensuring reliable performance in adverse conditions.
Sony G Master
- Build Quality: G Master lenses are built with high-quality materials, often using a mix of metal and engineering plastics for weight reduction and durability.
- Weather-Sealing: GM lenses are well-sealed, but some users have noted that certain models, particularly older ones, may not have as extensive sealing as their Canon or Nikon counterparts. Newer GM lenses have improved weather-sealing to match the rigorous demands of professional use.
Fujifilm XF and GF
- Build Quality: Fujifilm’s XF lenses are well-constructed, often using metal barrels and focusing rings, which offer a premium feel. GF lenses for the medium format system are even more robust, built to withstand the rigors of professional use.
- Weather-Sealing: Many XF and most GF lenses are weather-sealed, providing protection against dust, moisture, and cold temperatures. However, the sealing might not be as comprehensive as found in Canon L or Nikon’s high-end lenses.
5. Overall Performance and Superiority
- Canon L Series: Known for excellent build quality, extensive weather-sealing, and superior optical performance. Canon’s L series lenses excel in color accuracy, low distortion, and robust construction, making them ideal for professional use across various genres.
- Nikon NIKKOR (S-Line): Nikon’s S-Line lenses for mirrorless cameras are comparable to Canon’s L series in terms of image quality, AF performance, and build. NIKKOR lenses often excel in sharpness and handling chromatic aberration, particularly in their telephoto and prime lenses.
- Sony G Master: Sony’s GM lenses are known for their exceptional sharpness, smooth bokeh, and advanced autofocus technology. They often have an edge in AF speed and precision, especially when paired with Sony’s high-end mirrorless cameras. GM lenses are generally considered equal or superior to L series lenses in resolution and AF performance.
- Fujifilm XF and GF: Fujifilm’s lenses are unique in their rendering and color science. XF lenses are among the best for APS-C cameras, and GF lenses set a high standard for medium format optics. While their AF performance might not match Sony or Canon, their build quality and optical performance are highly regarded.
Conclusion
Each brand’s top-tier lens lineup has its strengths:
- Canon L series lenses are celebrated for their durability, versatile lineup, and excellent optical quality across various focal lengths.
- Nikon NIKKOR lenses offer superb sharpness, innovative lens elements, and reliable weather-sealing, especially in the S-Line for mirrorless cameras.
- Sony G Master lenses excel in resolution, autofocus performance, and bokeh quality, making them a top choice for mirrorless shooters.
- Fujifilm XF and GF lenses provide exceptional quality for APS-C and medium format systems, with excellent build quality and image performance, though their autofocus may not be as competitive.
The “superiority” of each brand’s lenses largely depends on specific needs and preferences, such as autofocus speed, handling, durability, and image rendering.
Which is why the next category is important.
Are L-Series lenses compatible with all Canon EOS cameras?
Yes, L-Series lenses are designed to be compatible with a wide range of Canon EOS cameras, ensuring you can enjoy their exceptional performance no matter which Canon camera you own.
Do L-Series lenses come with a warranty?
Yes, Canon typically provides a warranty for L-Series lenses, offering added peace of mind for your investment.
Can I use L-Series lenses for videography as well?
Absolutely! L-Series lenses are known for their exceptional optical quality, making them a great choice for videographers who demand top-notch performance.
Are L-Series lenses heavy?
Some L-Series lenses can be heavy due to their robust construction and large glass elements. However, the weight varies depending on the specific lens model.
